Welcome to the first installment of my blog series on the health, safety, and environmental (HSE) regulatory landscape across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
In this first article, I set the scene by providing:
- An overview of the GCC.
- Key HSE challenges across the GCC
- The most common findings from HSE regulatory compliance audits conducted across the region.
- Difficulties facing companies operating across the GCC in complying with HSE regulations.
In the following posts of this series, we present:
- A description of the international and regional agreements related to health & safety and environmental management within the GCC.
- An overview of the overarching worker health & safety and environmental legislation and the key regulatory authorities for each GCC member state.
- A review of the HSE regulatory requirements for each GCC member state.
- A deep dive into specific HSE legislation and regulations for each GCC member state.
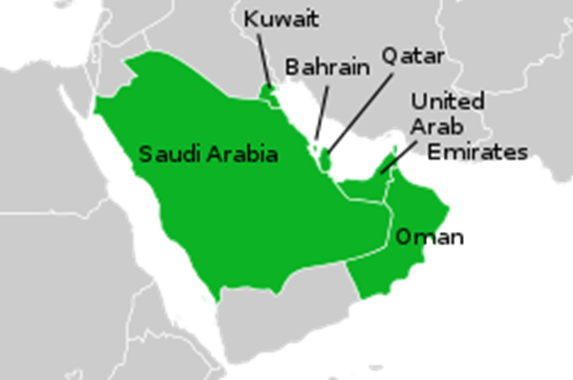
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
The GCC is a regional intergovernmental organization consisting of six member states: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). These countries are home to some of the largest and most influential industries in the world, with oil and gas being the most dominant sector. The region is responsible for producing a significant portion of the world’s oil and gas, with Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar being the largest oil producers in the region.
The GCC member states are also major players in the finance industry, with Bahrain serving as a regional financial hub and Dubai emerging as a global financial center. The real estate and hospitality industries are also major contributors to the GCC economy, driven by the region’s rapid urbanization and tourism growth. Construction is another significant sector, driven by the region’s extensive infrastructure development, including the construction of airports, ports, and rail networks.
The GCC member states have also made significant investments in diversifying their economies and promoting non-oil sectors, such as renewable energy, technology, and manufacturing.
HSE Challenges Across the GCC
The rapid economic growth across the GCC member states has brought about many benefits, such as increased prosperity, higher living standards, and improved infrastructure. However, this growth has also led to significant challenges in dealing with worker health and safety issues and environmental issues within the member states.
One of the main challenges related to worker health and safety is the rapid expansion of industries, particularly those in the construction and manufacturing sectors. The demand for new infrastructure and real estate has led to an influx of migrant workers, who may be vulnerable to exploitation and unsafe working conditions. These workers often lack access to proper safety equipment, training, and medical care, which can lead to accidents, injuries, and fatalities on worksites.
In addition, the rapid economic growth has put significant pressure on the environment, particularly in terms of air and water pollution. The region’s heavy reliance on oil and gas as a primary source of revenue has resulted in high levels of air pollution, which can have significant health impacts on workers and residents in the surrounding areas. The rapid urbanization and industrialization have also led to increased demand for water resources, resulting in over-extraction of groundwater and depletion of aquifers.
Moreover, the GCC member states face challenges related to waste management, including inadequate infrastructure for collecting and disposing of waste, and lack of public awareness about proper waste management practices. This has led to the accumulation of waste in landfills and illegal dumping, which can contribute to environmental degradation and public health hazards.
Common Non-Compliance Findings
We have conducted hundreds of HSE regulatory audits over the past two decades across all countries in the GCC for our multi-national clients, which have included a wide range of industries such as manufacturing, food and beverage, logistics and warehousing, oil and gas services, contracting, data centers, offices and retail stores.
Common findings of non-compliance with HSE regulations from these audits include:
- Lack of training: Insufficient training and awareness programs for employees on health and safety procedures, including for instance lack of information in Arabic language.
- Insufficient First Aid: Lack of first aid equipment and inspection of first aid kits, lack of trained first aiders.
- Improper Hazardous Materials Management: Improper storage and handling of hazardous materials, such as improperly segregated materials or lack of spill response kits or contents.
- Poor Housekeeping: Poor housekeeping practices leading to slip, trip, and fall hazards.
- Inadequate fire safety measures: Lack of signage, improper placement/blocking of fire extinguishers and lack of evacuation plans are not uncommon.
- Improper waste management and disposal practices: Mixing of different waste streams, improper classification of hazardous wastes, and lack of waste manifests.
- Non-compliance with electrical safety standards: Unsafe use of electrical equipment, lack of proper grounding, and extension cords used for permanent equipment.
- Lack of proper PPE (personal protective equipment): for workers handling hazardous materials.
- Lack of procedures: Such as lone-worker and safe driving procedures.
- Insufficient noise control: Leading to high noise levels within the facility that can impact workers and at the site boundary that can impact neighbors.
Challenges in Complying with HSE Regulations:
There are several reasons why companies operating in the GCC have difficulty in complying with HSE regulations:
- Lack of awareness: Many companies may not be aware of the regulations and standards related to HSE within their jurisdiction, or they may not fully understand their obligations under these regulations.
- Cultural differences: Some companies may come from cultures where health and safety standards are not as strict as in the GCC, making it difficult for them to adapt to the local regulations.
- Language barriers: Employees that do not have a good command of the local language may have difficulty understanding and complying with the regulations.
- Limited resources: Some companies may lack the financial and human resources to invest in HSE measures, such as training, equipment, and facilities.
- Lack of enforcement: Despite the presence of regulations and standards, enforcement can be weak in some areas, which can create a perception that HSE compliance is not a high priority.
- Rapid growth: The rapid pace of economic growth in the GCC has led to a proliferation of new businesses, which can make it difficult for regulatory bodies to keep up with the pace of development and ensure that all companies are complying with the regulations.
In the next article of this series, I will discuss the international and regional agreements related to worker health & safety and environmental management within the GCC
As always, feel free to contact us if you need help with your HSE challenges at your site.
Thanks for reading. Keep safe. Be healthy. Respect your environment.
I hope that you will bookmark the blog, share it with your colleagues and visit the blog frequently because you find it informative and helpful. I value your feedback and suggestions for future topics.
Please enter your email in the box at the top of the post and subscribe to our blog HSE Asia – our weekly blog will be emailed directly to you.
Photo Credits: Image from Wikipedia (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gulf_Cooperation_Council.svg)
- Is Your Business Compliant with HSE Regulations? Take Our Quiz to Find Out! - September 16, 2024
- Duty of Care: What it Is and What it Means to Companies Operating in the GCC? - January 28, 2024
- Free E-Book:Health, Safety, and Environment Regulatory Review – United Arab Emirates: An Overview of Federal Requirements - July 5, 2023